json
Reads structured data from a JSON file.
The file must contain a valid JSON value, such as object or array. The JSON values will be converted into corresponding Typst values as listed in the table below.
The function returns a dictionary, an array or, depending on the JSON file, another JSON data type.
The JSON files in the example contain objects with the keys temperature,
unit, and weather.
Example
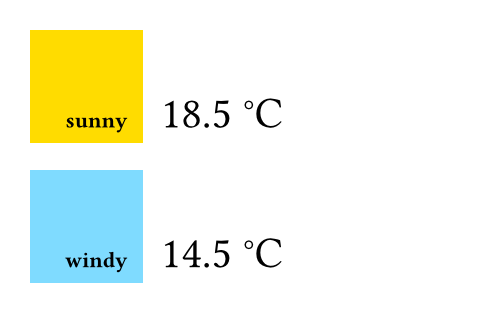
#let forecast(day) = block[
#box(square(
width: 2cm,
inset: 8pt,
fill: if day.weather == "sunny" {
yellow
} else {
aqua
},
align(
bottom + right,
strong(day.weather),
),
))
#h(6pt)
#set text(22pt, baseline: -8pt)
#day.temperature °#day.unit
]
#forecast(json("monday.json"))
#forecast(json("tuesday.json"))
Conversion details
| JSON value | Converted into Typst |
|---|---|
null | none |
| bool | bool |
| number | float or int |
| string | str |
| array | array |
| object | dictionary |
| Typst value | Converted into JSON |
|---|---|
| types that can be converted from JSON | corresponding JSON value |
bytes | string via repr |
symbol | string |
content | an object describing the content |
other types (length, etc.) | string via repr |
Notes
-
In most cases, JSON numbers will be converted to floats or integers depending on whether they are whole numbers. However, be aware that integers larger than 263-1 or smaller than -263 will be converted to floating-point numbers, which may result in an approximative value.
-
Bytes are not encoded as JSON arrays for performance and readability reasons. Consider using
cbor.encodefor binary data. -
The
reprfunction is for debugging purposes only, and its output is not guaranteed to be stable across Typst versions.
Parameters
source
A path to a JSON file or raw JSON bytes.
Definitions
decodejson.decode is deprecated, directly pass bytes to json instead; it will be removed in Typst 0.15.0
Reads structured data from a JSON string/bytes.
data
JSON data.
encode
Encodes structured data into a JSON string.
value any Required Positional
Value to be encoded.
pretty
Whether to pretty print the JSON with newlines and indentation.
Default: true