stackElement
Arranges content and spacing horizontally or vertically.
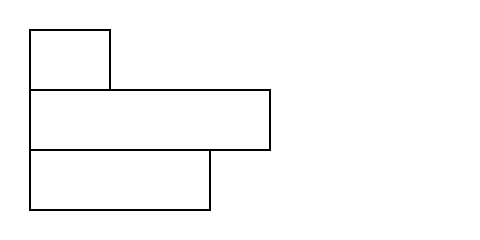
The stack places a list of items along an axis, with optional spacing between each item.
Example
#stack(
dir: ttb,
rect(width: 40pt),
rect(width: 120pt),
rect(width: 90pt),
)
Accessibility
Stacks do not carry any special semantics. The contents of the stack are read by Assistive Technology (AT) in the order in which they have been passed to this function.
Parameters
dir
The direction along which the items are stacked. Possible values are:
ltr: Left to right.rtl: Right to left.ttb: Top to bottom.btt: Bottom to top.
You can use the start and end methods to obtain the initial and
final points (respectively) of a direction, as alignment. You can also
use the axis method to determine whether a direction is
"horizontal" or "vertical". The inv method returns a
direction's inverse direction.
For example, ttb.start() is top, ttb.end() is bottom,
ttb.axis() is "vertical" and ttb.inv() is equal to btt.
Default: ttb
spacing
Spacing to insert between items where no explicit spacing was provided.
Default: none
children
The children to stack along the axis.